SCOPUS
KCI등재
SCIE
Antibiotic resistance fate in the full-scale drinking water and municipal wastewater treatment processes: A review
-
저자
Rui Gao (State Key Laboratory of Pollution Control and Resource Reuse, Shanghai Institute of Pollution Control and Ecological Security, Tongji Univ., China) ; Minghao Sui (State Key Laboratory of Pollution Control and Resource Reuse, Shanghai Institute of Pollution Control and Ecological Security, Tongji Univ., China)
-
발행기관
-
학술지명
-
권호사항
-
발행연도
2021
-
작성언어
English
-
주제어
-
등재정보
SCOPUS,KCI등재,SCIE
-
자료형태
학술저널
-
수록면
173-193(21쪽)
-
KCI 피인용횟수
0
-
DOI식별코드
-
제공처
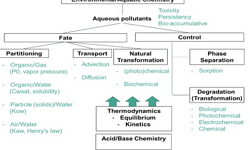
Antibiotic-resistant bacteria (ARB) and antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs) have been widely identified as emerging pollutants in various aquatic compartments. Concerns have been raised that the antibiotic resistance determinants may occur in treated drinking water and wastewater, weakening the therapeutic efficacy of antibiotics and so posing threat to public health. Most often, laboratory trials are conducted to assess the removal efficiency of ARB and ARGs in individual treatment processes (e.g., disinfection). However, the random variations of microbial distribution and chemical compositions in real-world environments cannot be entirely simulated, presumably leading to false-positive results as a consequence. It is therefore useful to provide a summary of recent advancements regarding the antibiotic resistance attenuation during full-scale water/wastewater treatments, which has not been adequately evaluated so far. In this review, the prevalence, proliferation and transmission of ARB and ARGs in urban water cycle, coupled with corresponding detection methods are presented as a short overview. The fate of ARB and ARGs in the sequential drinking water and wastewater processing units is critically summarized, the aim of which is to provide guidance for improving the current water treatment facilities to further reduce the antibiotic resistance in finished water.
더보기- ABSTRACT
- 1. Introduction
- 2. The Prevalence of ARB/ARGs in Urban Water Cycle
- 3. Common Methods of ARB/ARGs Detection in Drinking Water/Waste Water Systems
- 4. The Fate of Antibiotic Resistance in Full-scale Drinking Water/Wastewater Treatment Plants
- 5. Conclusions
- References
- 1 Peltier E, "Zinc-induced antibiotic resistance in activated sludge bioreactors" 44 (44): 3829-3836, 2010
- 2 Douterelo I, "Whole metagenome sequencing of chlorinated drinking water distribution systems" 4 (4): 2080-2091, 2018
- 3 WHO, "WHO publishes list of bacteria for which new antibiotics are urgently needed" WHO
- 4 Varela AR, "Vancomycin resistant enterococci : From the hospital effluent to the urban wastewater treatment plant" 450 : 155-161, 2013
- 5 Rizzo L, "Urban wastewater treatment plants as hotspots for antibiotic resistant bacteria and genes spread into the environment : a review" 447 : 345-360, 2013
- 6 Berglund B, "Urban wastewater effluent increases antibiotic resistance gene concentrations in a receiving northern European river" 34 (34): 192-196, 2015
- 7 Egervärn M, "Unexpected common occurrence of transferable extended spectrum cephalosporinase-producing Escherichia coli in Swedish surface waters used for drinking water supply" 587 : 466-472, 2017
- 8 Vaz-Moreira I, "Ubiquitous and persistent Proteobacteria and other Gram-negative bacteria in drinking water" 586 : 1141-1149, 2017
- 9 Luo Y, "Trends in Antibiotic Resistance Genes Occurrence in the Haihe River, China" 44 (44): 7220-7225, 2010
- 10 Aali R, "Tracking of chloramphenicol, erythromycin, and sulfamethoxazole antibiotic-resistant bacteria from untreated wastewater effluents to receiving river" 6 (6): 89-96, 2019
- 11 Leu S-Y, "Toward Long Solids Retention Time of Activated Sludge Processes : Benefits in Energy Saving, Effluent Quality, and Stability" 84 (84): 42-53, 2012
- 12 Chen B, "The role of class I integrons in the dissemination of sulfonamide resistance genes in the Pearl River and Pearl River Estuary, South China" 282 : 61-67, 2015
- 13 Chen JH, "The preozonation of phenolic aqueous solution and its effect on the improvement of coagulation treatment" 25 (25): 323-333, 2003
- 14 Calero-Cáceres W, "The occurrence of antibiotic resistance genes in a Mediterranean river and their persistence in the riverbed sediment" 223 : 384-394, 2017
- 15 Garcia S, "The effect of wastewater treatment on antibiotic resistance in Escherichia coli and Enterococcus sp" 79 (79): 2387-2395, 2007
- 16 Bai X, "The drinking water treatment process as a potential source of affecting the bacterial antibiotic resistance" 533 : 24-31, 2015
- 17 Quach-Cu J, "The Effect of Primary, Secondary, and Tertiary Wastewater Treatment Processes on Antibiotic Resistance Gene (ARG) Concentrations in Solid and Dissolved Wastewater Fractions" 10 (10): 2018
- 18 Miranda AC, "Surface water disinfection by chlorination and advanced oxidation processes:inactivation of an antibiotic resistant E. coli strain and cytotoxicity evaluation" 554 : 1-6, 2016
- 19 Zhang Y, "Subinhibitory Concentrations of Disinfectants Promote the Horizontal Transfer of Multidrug Resistance Genes within and across Genera" 51 (51): 570-580, 2017
- 20 Liu C, "Study on mechanism similarities and differences of bacteria removal in raw water by two types of coagulant" 35 (35): 361-, 2007
- 21 Petrovich ML, "Spatially resolved abundances of antibiotic resistance genes and intI1in wastewater treatment biofilms" 116 (116): 543-554, 2019
- 22 Doretto KM, "Sorption and desorption of sulfadimethoxine, sulfaquinoxaline and sulfamethazine antimicrobials in Brazilian soils" 476 : 406-414, 2014
- 23 Wang Y-K, "Simultaneous effective carbon and nitrogen removals and phosphorus recovery in an intermittently aerated membrane bioreactor integrated system" 5 : 2015
- 24 Wu D, "Simulated discharge of treated landfill leachates reveals a fueled development of antibiotic resistance in receiving tidal river" 114 : 143-151, 2018
- 25 Zhang M, "Selective antibiotic resistance genes in multiphase samples during biofilm growth in a simulated drinking water distribution system : Occurrence, correlation and low-pressure ultraviolet removal" 649 : 146-155, 2019
- 26 Knapp CW, "Seasonal variations in antibiotic resistance gene transport in the almendares river, havana, cuba" 3 : 396-, 2012
- 27 Rieke EL, "Seasonal variation of macrolide resistance gene abundances in the South Fork Iowa River Watershed" 610 : 1173-1179, 2018
- 28 Dhawde R, "Seasonal prevalence of antibiotic-resistant bacteria in the river Mula-Mutha, India" 190 (190): 533-, 2018
- 29 Son D-i, "Seasonal changes in antibiotic resistance genes in rivers and reservoirs in South Korea" 47 (47): 1079-1085, 2018
- 30 Beaber JW, "SOS response promotes horizontal dissemination of antibiotic resistance genes" 427 (427): 72-74, 2004
- 31 Zhu Y, "Robust performance of a membrane bioreactor for removing antibiotic resistance genes exposed to antibiotics : role of membrane foulants" 130 : 139-150, 2018
- 32 Zhang X, "Response of Anammox biofilm to antibiotics in trace concentration : Microbial activity, diversity and antibiotic resistance genes" 367 : 182-187, 2019
- 33 Lüddeke F, "Removal of total and antibiotic resistant bacteria in advanced wastewater treatment by ozonation in combination with different filtering techniques" 69 : 243-251, 2015
- 34 Dullemont Y, "Removal of microorganisms by slow sand filtration" 1 : 12-20, 2006
- 35 Grehs BW, "Removal of microorganisms and antibiotic resistance genes from treated urban wastewater : A comparison between aluminium sulphate and tannin coagulants" 166 : 115056-, 2019
- 36 McConnell MM, "Removal of antibiotic resistance genes in two tertiary level municipal wastewater treatment plants" 643 : 292-300, 2018
- 37 Li N, "Removal of antibiotic resistance genes from wastewater treatment plant effluent by coagulation" 111 : 204-212, 2017
- 38 Zhang TY, "Removal of antibiotic resistance genes and control of horizontal transfer risk by UV, chlorination and UV/chlorination treatments of drinking water" 358 : 589-597, 2019
- 39 Nielsen U, "Removal of APIs and bacteria from hospital wastewater by MBR plus O-3, O-3+ H2O2, PAC or ClO2" 67 (67): 854-862, 2013
- 40 Sha'arani S, "Removal efficiency of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria using a natural coagulant during coagulation, flocculation, and sedimentation processes" 80 (80): 1787-1795, 2019
- 41 Wu D, "Relationships between antibiotics and antibiotic resistance gene levels in municipal solid waste leachates in Shanghai, China" 49 (49): 4122-4128, 2015
- 42 Khan S, "Relationship between antibiotic-and disinfectant-resistance profiles in bacteria harvested from tap water" 152 : 132-141, 2016
- 43 Di Cesare A, "Rainfall increases the abundance of antibiotic resistance genes within a riverine microbial community" 226 : 473-478, 2017
- 44 Colomer-Lluch M, "Quinolone resistance genes(qnrA and qnrS)in bacteriophage particles from wastewater samples and the effect of inducing agents on packaged antibiotic resistance genes" 69 (69): 1265-1274, 2014
- 45 Lee J, "Quantitative and qualitative changes in antibiotic resistance genes after passing through treatment processes in municipal wastewater treatment plants" 605 : 906-914, 2017
- 46 Böckelmann U, "Quantitative PCR monitoring of antibiotic resistance genes and bacterial pathogens in three European artificial groundwater recharge systems" 75 (75): 154-163, 2009
- 47 Nerkar SS, "Quality of Water and Antibiotic Resistance of Escherichia coli from Water Sources of Hilly Tribal Villages with and without Integrated Watershed Management-A One Year Prospective Study" 11 (11): 6156-6170, 2014
- 48 Fakayode IB, "Quality assessment and prevalence of antibiotic resistant bacteria in government approved mini-water schemes in Southwest, Nigeria" 133 : 151-158, 2018
- 49 Hao H, "Profiling of intracellular and extracellular antibiotic resistance genes in tap water" 365 : 340-345, 2019
- 50 Zhang J, "Profiles and drivers of antibiotic resistance genes distribution in one-stage and two-stage sludge anaerobic digestion based on microwave-H2O2 pretreatment" 241 : 573-581, 2017
- 51 Guo X, "Prevalence of sulfonamide and tetracycline resistance genes in drinking water treatment plants in the Yangtze River Delta, China" 493 : 626-631, 2014
- 52 Stoll C, "Prevalence of clinically relevant antibiotic resistance genes in surface water samples collected from Germany and Australia" 46 (46): 9716-9726, 2012
- 53 Xi C, "Prevalence of antibiotic resistance in drinking water treatment and distribution systems" 75 (75): 5714-5718, 2009
- 54 Jiang L, "Prevalence of antibiotic resistance genes and their relationship with antibiotics in the Huangpu River and the drinking water sources, Shanghai, China" 458 : 267-272, 2013
- 55 Mao DQ, "Prevalence and proliferation of antibiotic resistance genes in two municipal wastewater treatment plants" 85 : 458-466, 2015
- 56 Kurasam J, "Presence of fluoroquinolone resistance with persistent occurrence of gyrA gene mutations in a municipal wastewater treatment plant in India" 211 : 817-825, 2018
- 57 Bergeron S, "Presence of antibiotic resistant bacteria and antibiotic resistance genes in raw source water and treated drinking water" 102 : 370-374, 2015
- 58 Bergeron S, "Presence of antibiotic resistance genes in raw source water of a drinking water treatment plant in a rural community of USA" 124 : 3-9, 2017
- 59 Dodd MC, "Potential impacts of disinfection processes on elimination and deactivation of antibiotic resistance genes during water and wastewater treatment" 14 (14): 1754-1771, 2012
- 60 Birosova L, "Pilot study of seasonal occurrence and distribution of antibiotics and drug resistant bacteria in wastewater treatment plants in Slovakia" 490 : 440-444, 2014
- 61 Ren S, "Photocatalytic reactive ultrafiltration membrane for removal of antibiotic resistant bacteria and antibiotic resistance genes from wastewater effluent" 52 (52): 8666-8673, 2018
- 62 Mao D, "Persistence of extracellular DNA in river sediment facilitates antibiotic resistance gene propagation" 48 (48): 71-78, 2013
- 63 Su HC, "Persistence of antibiotic resistance genes and bacterial community changes in drinking water treatment system : From drinking water source to tap water" 616 : 453-461, 2018
- 64 Lamba M, "Performance comparison of secondary and tertiary treatment systems for treating antibiotic resistance" 127 : 172-182, 2017
- 65 Gomes J, "Ozone and Photocatalytic Processes for Pathogens Removal from Water: A Review" 9 (9): 2019
- 66 Sousa JM, "Ozonation and UV254nm radiation for the removal of microorganisms and antibiotic resistance genes from urban wastewater" 323 : 434-441, 2017
- 67 Wang R-N, "Occurrence of super antibiotic resistance genes in the downstream of the Yangtze River in China : Prevalence and antibiotic resistance profiles" 651 : 1946-1957, 2019
- 68 Rodriguez-Mozaz S, "Occurrence of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes in hospital and urban wastewaters and their impact on the receiving river" 69 : 234-242, 2015
- 69 Edge TA, "Occurrence of antibiotic resistance in Escherichia coli from surface waters and fecal pollution sources near Hamilton, Ontario" 51 (51): 501-505, 2005
- 70 Zhang X-H, "Occurrence of antibiotic resistance genes in landfill leachate treatment plant and its effluent-receiving soil and surface water" 218 : 1255-1261, 2016
- 71 Nagulapally SR, "Occurrence of Ciprofloxacin-, Trimethoprim-Sulfamethoxazole-, and Vancomycin-Resistant Bacteria in a Municipal Wastewater Treatment Plant" 81 (81): 82-90, 2009
- 72 Zhang S, "Occurrence and variations of five classes of antibiotic resistance genes along the Jiulong River in southeast China" 34 (34): 345-, 2013
- 73 Su H, "Occurrence and temporal variation of antibiotic resistance genes(ARGs)in shrimp aquaculture : ARGs dissemination from farming source to reared organisms" 607 : 357-366, 2017
- 74 Hu Y, "Occurrence and removal of sulfonamide antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes in conventional and advanced drinking water treatment processes" 360 : 364-372, 2018
- 75 Hu Y, "Occurrence and reduction of antibiotic resistance genes in conventional and advanced drinking water treatment processes" 669 : 777-784, 2019
- 76 Li AL, "Occurrence and distribution of antibiotic resistance genes in the sediments of drinking water sources, urban rivers, and coastal areas in Zhuhai, China" 25 (25): 26209-26217, 2018
- 77 Aali R, "OCCURRENCE OF TETRACYCLINE RESISTANT BACTERIA AND RESISTANCE GENE (tetW) IN HOSPITAL AND MUNICIPAL WASTEWATERS" 23 (23): 2560-2566, 2014
- 78 Ma L, "New insights into antibiotic resistome in drinking water and management perspectives : A metagenomic based study of small-sized microbes" 152 : 191-201, 2019
- 79 Titilawo Y, "Multiple antibiotic resistance indexing of Escherichia coli to identify high-risk sources of faecal contamination of water" 22 (22): 10969-10980, 2015
- 80 Wen Q, "Monitoring and evaluation of antibiotic resistance genes in four municipal wastewater treatment plants in Harbin, Northeast China" 212 : 34-40, 2016
- 81 Li ZH, "Mitigated membrane fouling and enhanced removal of extracellular antibiotic resistance genes from wastewater effluent via an integrated pre-coagulation and microfiltration process" 159 : 145-152, 2019
- 82 Petrovich ML, "Microbial and Viral Communities and Their Antibiotic Resistance Genes Throughout a Hospital Wastewater Treatment System" 11 : 13-, 2020
- 83 Wangai FK, "Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in East Africa: red alert or red herring?" 19 : 596-605, 2019
- 84 Christgen B, "Metagenomics shows that low-energy anaerobic-aerobic treatment reactors reduce antibiotic resistance gene levels from domestic wastewater" 49 (49): 2577-2584, 2015
- 85 Shi P, "Metagenomic insights into chlorination effects on microbial antibiotic resistance in drinking water" 47 (47): 111-120, 2013
- 86 Lekunberri I, "Metagenomic exploration reveals a marked change in the river resistome and mobilome after treated wastewater discharges" 234 : 538-542, 2018
- 87 Guo J, "Metagenomic analysis reveals wastewater treatment plants as hotspots of antibiotic resistance genes and mobile genetic elements" 123 : 468-478, 2017
- 88 Gomez-Alvarez V, "Metagenomic analyses of drinking water receiving different disinfection treatments" 78 (78): 6095-6102, 2012
- 89 Xu L, "Mechanisms of ultraviolet disinfection and chlorination of Escherichia coli : Culturability, membrane permeability, metabolism, and genetic damage" 65 : 356-366, 2018
- 90 Szekeres E, "Investigating antibiotics, antibiotic resistance genes, and microbial contaminants in groundwater in relation to the proximity of urban areas" 236 : 734-744, 2018
- 91 Czekalski N, "Inactivation of antibiotic resistant bacteria and resistance genes by ozone : from laboratory experiments to full-scale wastewater treatment" 50 (50): 11862-11871, 2016
- 92 Zhang Y, "Inactivation of antibiotic resistance genes in municipal wastewater effluent by chlorination and sequential UV/chlorination disinfection" 512 : 125-132, 2015
- 93 Yoon Y, "Inactivation efficiency of plasmid-encoded antibiotic resistance genes during water treatment with chlorine, UV, and UV/H2O2" 123 : 783-793, 2017
- 94 Zheng G, "Importance of sludge conditioning in attenuating antibiotic resistance : Removal of antibiotic resistance genes by bioleaching and chemical conditioning with Fe [III]/CaO" 152 : 61-73, 2019
- 95 Garner E, "Impact of blending for direct potable reuse on premise plumbing microbial ecology and regrowth of opportunistic pathogens and antibiotic resistant bacteria" 151 : 75-86, 2019
- 96 Hirani ZM, "Impact of MBR cleaning and breaching on passage of selected microorganisms and subsequent inactivation by free chlorine" 57 : 313-324, 2014
- 97 Zanotto C, "Identification of antibiotic-resistant Escherichia coli isolated from a municipal wastewater treatment plant" 164 : 627-633, 2016
- 98 Lerminiaux NA, "Horizontal transfer of antibiotic resistance genes in clinical environments" 65 (65): 34-44, 2019
- 99 Xu L, "High-throughput profiling of antibiotic resistance genes in drinking water treatment plants and distribution systems" 213 : 119-126, 2016
- 100 Chen Y, "High-throughput profiling of antibiotic resistance gene dynamic in a drinking water river-reservoir system" 149 : 179-189, 2019
- 101 Aljerf L, "High-efficiency extraction of bromocresol purple dye and heavy metals as chromium from industrial effluent by adsorption onto a modified surface of zeolite : Kinetics and equilibrium study" 225 : 120-132, 2018
- 102 Klein EY, "Global increase and geographic convergence in antibiotic consumption between 2000 and 2015" 115 (115): E3463-E3470, 2018
- 103 Wang J, "Fate and proliferation of typical antibiotic resistance genes in five full-scale pharmaceutical wastewater treatment plants" 526 : 366-373, 2015
- 104 Lu X-M, "Fate and abundance of antibiotic resistance genes on microplastics in facility vegetable soil" 709 : 2020
- 105 Lv L, "Exposure to mutagenic disinfection byproducts leads to increase of antibiotic resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa" 48 (48): 8188-8195, 2014
- 106 Tao CW, "Evaluation of five antibiotic resistance genes in wastewater treatment systems of swine farms by real-time PCR" 496 : 116-121, 2014
- 107 Skariyachan S, "Environmental monitoring of bacterial contamination and antibiotic resistance patterns of the fecal coliforms isolated from Cauvery River, a major drinking water source in Karnataka, India" 187 (187): 279-, 2015
- 108 Zhang S-X, "Emission and fate of antibiotics in the Dongjiang River Basin, China: Implication for antibiotic resistance risk" 136518-, 2020
- 109 Bengtsson-Palme J, "Elucidating selection processes for antibiotic resistance in sewage treatment plants using metagenomics" 572 : 697-712, 2016
- 110 Chen H, "Effects of Advanced Treatment Systems on the Removal of Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Wastewater Treatment Plants from Hangzhou, China" 47 (47): 8157-8163, 2013
- 111 Zheng J, "Effects and mechanisms of ultraviolet, chlorination, and ozone disinfection on antibiotic resistance genes in secondary effluents of municipal wastewater treatment plants" 317 : 309-316, 2017
- 112 Huang J-J, "Effect of chlorination and ultraviolet disinfection on tetA-mediated tetracycline resistance of Escherichia coli" 90 (90): 2247-2253, 2013
- 113 Ma X, "Effect of Water Treatment Process on the Bacterial Multidrug Resistance in Drinking Water" 37 (37): 4235-4240, 2016
- 114 Suzuki S, "Editorial : Antibiotic Resistance in Aquatic Systems" 8 : 1-3, 2017
- 115 Sui Q, "Does the biological treatment or membrane separation reduce the antibiotic resistance genes from swine wastewater through a sequencing-batch membrane bioreactor treatment process" 118 : 274-281, 2018
- 116 Czekalski N, "Does human activity impact the natural antibiotic resistance background? Abundance of antibiotic resistance genes in 21Swiss lakes" 81 : 45-55, 2015
- 117 Vaz-Moreira I, "Diversity and antibiotic resistance patterns of Sphingomonadaceae isolates from drinking water" 77 (77): 5697-5706, 2011
- 118 Figueira V, "Diversity and antibiotic resistance of Aeromonas spp. in drinking and waste water treatment plants" 45 (45): 5599-5611, 2011
- 119 Narciso-da-Rocha C, "Diversity and antibiotic resistance of Acinetobacter spp. in water from the source to the tap" 97 (97): 329-340, 2013
- 120 Stange C, "Distribution of clinically relevant antibiotic resistance genes in Lake Tai, China" 655 : 337-346, 2019
- 121 Ben W, "Distribution of antibiotic resistance in the effluents of ten municipal wastewater treatment plants in China and the effect of treatment processes" 172 : 392-398, 2017
- 122 Hu Y, "Distribution characteristics of sulfonamide antibiotic resistance genes in a drinking water source in East China" 39 (39): 4222-4228, 2018
- 123 Lu J, "Distribution and abundance of antibiotic resistance genes in sand settling reservoirs and drinking water treatment plants across the Yellow River, China" 10 (10): 246-, 2018
- 124 Wang J, "Dissemination of veterinary antibiotics and corresponding resistance genes from a concentrated swine feedlot along the waste treatment paths" 92 : 317-323, 2016
- 125 Huang L, "Dissemination of antibiotic resistance genes(ARGs)by rainfall on a cyclic economic breeding livestock farm" 138 : 114-121, 2019
- 126 Von Wintersdorff CJH, "Dissemination of Antimicrobial Resistance in Microbial Ecosystems through Horizontal Gene Transfer" 7 : 2016
- 127 He L-Y, "Dissemination of Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Representative Broiler Feedlots Environments : Identification of Indicator ARGs and Correlations with Environmental Variables" 48 (48): 13120-13129, 2014
- 128 He LY, "Discharge of swine wastes risks water quality and food safety: Antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes, from swine sources to the receiving environments" 92-93 : 210-219, 2016
- 129 Knapp CW, "Differential fate of erythromycin and beta-lactam resistance genes from swine lagoon waste under different aquatic conditions" 158 (158): 1506-1512, 2010
- 130 Pallares-Vega R, "Determinants of presence and removal of antibiotic resistance genes during WWTP treatment : A cross-sectional study" 161 : 319-328, 2019
- 131 Fernando DM, "Detection of antibiotic resistance genes in source and drinking water samples from a First Nations Community in Canada" 82 (82): 4767-4775, 2016
- 132 Tao R, "Detection of antibiotic resistance and tetracycline resistance genes in Enterobacteriaceae isolated from the Pearl rivers in South China" 158 (158): 2101-2109, 2010
- 133 He H, "Degradation and deactivation of bacterial antibiotic resistance genes during exposure to free chlorine, monochloramine, chlorine dioxide, ozone, ultraviolet light, and hydroxyl radical" 53 (53): 2013-2026, 2019
- 134 Zhang J, "Deciphering the factors influencing the discrepant fate of antibiotic resistance genes in sludge and water phases during municipal wastewater treatment" 265 : 310-319, 2018
- 135 Coleman BL, "Contamination of Canadian private drinking water sources with antimicrobial resistant Escherichia coli" 47 (47): 3026-3036, 2013
- 136 Di Cesare A, "Constitutive presence of antibiotic resistance genes within the bacterial community of a large subalpine lake" 24 (24): 3888-3900, 2015
- 137 Zhang Q-Q, "Comprehensive Evaluation of Antibiotics Emission and Fate in the River Basins of China : Source Analysis, Multimedia Modeling, and Linkage to Bacterial Resistance" 49 (49): 6772-6782, 2015
- 138 Oh J, "Comparison of different disinfection processes in the effective removal of antibiotic-resistant bacteria and genes" 26 (26): 1238-1242, 2014
- 139 Pak G, "Comparison of antibiotic resistance removal efficiencies using ozone disinfection under different pH and suspended solids and humic substance concentrations" 50 (50): 7590-7600, 2016
- 140 Jong M-C, "Co-optimization of sponge-core bioreactors for removing total nitrogen and antibiotic resistance genes from domestic wastewater" 634 : 1417-1423, 2018
- 141 Yu Z, "Co-occurrence of mobile genetic elements and antibiotic resistance genes in municipal solid waste landfill leachates : a preliminary insight into the role of landfill age" 106 : 583-592, 2016
- 142 Makowska N, "Class 1 integrase, sulfonamide and tetracycline resistance genes in wastewater treatment plant and surface water" 144 : 1665-1673, 2016
- 143 Hou AM, "Chlorine injury enhances antibiotic resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa through over expression of drug efflux pumps" 156 : 366-371, 2019
- 144 Uyaguari MI, "Characterization and quantitation of a novel β-lactamase gene found in a wastewater treatment facility and the surrounding coastal ecosystem" 77 (77): 8226-8233, 2011
- 145 Shi Y, "Characteristics of ARG-carrying plasmidome in the cultivable microbial community from wastewater treatment system under high oxytetracycline concentration" 102 (102): 1847-1858, 2018
- 146 Lefkowitz JR, "Changes in antibiotic resistance patterns of Escherichia coli during domestic wastewater treatment" 81 (81): 878-885, 2009
- 147 Hrenovic J, "Carbapenem-resistant bacteria in a secondary wastewater treatment plant" 43 (43): 186-191, 2017
- 148 Lamba M, "Carbapenem resistance exposures via wastewaters across New Delhi" 119 : 302-308, 2018
- 149 Harrison KR, "Benzalkonium chloride alters phenotypic and genotypic antibiotic resistance profiles in a source water used for drinking water treatment" 257 : 113472-, 2020
- 150 Oluyege J, "Bacteriological and physico-chemical quality assessment of household drinking water in Ado-Ekiti, Nigeria" 11 (11): 79-84, 2011
- 151 Krasovec R, "Bacterial multicellularity as a possible source of antibiotic resistance" 60 (60): 484-488, 2003
- 152 Jia S, "Bacterial community shift drives antibiotic resistance promotion during drinking water chlorination" 49 (49): 12271-12279, 2015
- 153 Leginowicz M, "BIODIVERSITY AND ANTIBIOTIC RESISTANCE OF BACTERIA ISOLATED FROM TAP WATER IN WROCLAW, POLAND" 44 (44): 85-98, 2018
- 154 Chao C-C, "Assessment of a Sensitive qPCR Assay Targeting a Multiple-Copy Gene to Detect Orientia tsutsugamushi DNA" 4 (4): 2019
- 155 Chang F, "Antimicrobial resins with quaternary ammonium salts as a supplement to combat the antibiotic resistome in drinking water treatment plants" 221 : 132-140, 2019
- 156 Liu X, "Antibiotics in the aquatic environments : A review of lakes, China" 627 : 1195-1208, 2018
- 157 Yang Y, "Antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes in global lakes : A review and meta-analysis" 116 : 60-73, 2018
- 158 Li J, "Antibiotic-resistant genes and antibiotic-resistant bacteria in the effluent of urban residential areas, hospitals, and a municipal wastewater treatment plant system" 22 (22): 4587-4596, 2015
- 159 Zheng J, "Antibiotic resistome promotion in drinking water during biological activated carbon treatment:Is it influenced by quorum sensing?" 612 : 1-8, 2018
- 160 Bai Y, "Antibiotic resistome profile based on metagenomics in raw surface drinking water source and the influence of environmental factor : A case study in Huaihe River Basin, China" 248 : 438-447, 2019
- 161 Thevenon F, "Antibiotic resistant bacteria/genes dissemination in lacustrine sediments highly increased following cultural eutrophication of Lake Geneva(Switzerland)" 86 (86): 468-476, 2012
- 162 Turolla A, "Antibiotic resistant bacteria in urban sewage : Role of full-scale wastewater treatment plants on environmental spreading" 191 : 761-769, 2018
- 163 Khan S, "Antibiotic resistant bacteria found in municipal drinking water" 3 (3): 541-552, 2016
- 164 Amador PP, "Antibiotic resistance in wastewater : Occurrence and fate of Enterobacteriaceae producers of Class A and Class C β-lactamases" 50 (50): 26-39, 2015
- 165 Manaia CM, "Antibiotic resistance in urban aquatic environments: can it be controlled?" 100 (100): 1543-1557, 2016
- 166 Faria C, "Antibiotic resistance in coagulase negative staphylococci isolated from wastewater and drinking water" 407 (407): 3876-3882, 2009
- 167 Xiong W, "Antibiotic resistance genes occurrence and bacterial community composition in the Liuxi River" 2 : 61-, 2014
- 168 Zhang X-X, "Antibiotic resistance genes in water environment" 82 (82): 397-414, 2009
- 169 Neudorf KD, "Antibiotic resistance genes in municipal wastewater treatment systems and receiving waters in Arctic Canada" 598 : 1085-1094, 2017
- 170 Sanderson H, "Antibiotic resistance genes as an emerging environmental contaminant" 24 (24): 205-218, 2016
- 171 Xu L, "Antibiotic resistance genes and microcystins in a drinking water treatment plant" 258 : 113718-, 2020
- 172 Mispagel H, "Antibiotic resistance from wastewater oxidation ponds" 77 (77): 2996-3002, 2005
- 173 Kumar S, "Antibiotic resistance and genetic diversity in water-borne Enterobacteriaceae isolates from recreational and drinking water sources" 10 (10): 789-798, 2013
- 174 Schreiber C, "Antibiotic resistance among autochthonous aquatic environmental bacteria" 67 (67): 117-123, 2013
- 175 Hiller C, "Antibiotic microbial resistance (AMR) removal efficiencies by conventional and advanced wastewater treatment processes:A review" 685 : 596-608, 2019
- 176 Zhang H, "Antibiotic Resistome Alteration by Different Disinfection Strategies in a Full-Scale Drinking Water Treatment Plant Deciphered by Metagenomic Assembly" 53 (53): 2141-2150, 2019
- 177 Lien LTQ, "Antibiotic Resistance and Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Escherichia coli Isolates from Hospital Wastewater in Vietnam" 14 (14): 2017
- 178 Kinge CNW, "Antibiotic Resistance Profiles of Escherichia Coli Isolated from Different Water Sources in the Mmabatho Locality, North-West Province" 106 (106): 44-49, 2010
- 179 Lepesova K, "Annual changes in the occurrence of antibiotic-resistant coliform bacteria and enterococci in municipal wastewater" 26 (26): 18470-18483, 2019
- 180 Aljerf L, "Advanced highly polluted rainwater treatment process" 12 : 50-58, 2018
- 181 Couch M, "Abundances of tetracycline resistance genes and tetracycline antibiotics during anaerobic digestion of swine waste" 48 (48): 171-178, 2019
- 182 Rafraf ID, "Abundance of antibiotic resistance genes in five municipal wastewater treatment plants in the Monastir Governorate, Tunisia" 219 : 353-358, 2016
- 183 Koczura R, "Abundance of Class 1 Integron-Integrase and Sulfonamide Resistance Genes in River Water and Sediment Is Affected by Anthropogenic Pressure and Environmental Factors" 72 (72): 909-916, 2016
- 184 Wang L, "Abundance and removal of antibiotic resistance genes(ARGs)in the rearing environments of intensive shrimp aquaculture in South China" 54 (54): 211-218, 2019
- 185 Besharati S, "A survey on microbial quality and antibiotic resistance in Karoon River, Khuzestan, Iran" 8 (8): 146-, 2018
- 186 Börjesson S, "A seasonal study of the mecA gene and Staphylococcus aureus including methicillin-resistant S. aureus in a municipal wastewater treatment plant" 43 (43): 925-932, 2009
- 187 Waldor MK, "A new type of conjugative transposon encodes resistance to sulfamethoxazole, trimethoprim, and streptomycin in Vibrio cholerae O139" 178 (178): 4157-4165, 1996
-
The methodological approach to environmental risk assessment from man-made emergencies at chemically hazardous sites
- 대한환경공학회
- Pavel V. Yemelin
- 2021
- SCOPUS,KCI등재,SCIE
-
Multi-linear regression model for chlorine consumption by waters
- 대한환경공학회
- Guocheng Zhu
- 2021
- SCOPUS,KCI등재,SCIE
-
Fabrication of hierarchical Bentonite/Chitosan/NiFe₂O₄ ternary nanocomposite and its efficiency in the removal of Pb(II) from aqueous medium
- 대한환경공학회
- Debasish Guha Thakurata
- 2021
- SCOPUS,KCI등재,SCIE
-
A study on novel coupled membrane bioreactor with electro oxidation for biofouling reduction
- 대한환경공학회
- Kamalakannan Vasanthapalaniapp
- 2021
- SCOPUS,KCI등재,SCIE
분석정보
- 학술지 이력
학술지 이력 연월일 이력구분 이력상세 등재구분 2023 평가예정 해외DB학술지평가 신청대상 (해외등재 학술지 평가) 2020-01-01 평가 등재학술지 유지 (해외등재 학술지 평가) KCI등재 2010-01-01 평가 등재학술지 유지 (등재유지) KCI등재 2008-01-01 평가 등재학술지 유지 (등재유지) KCI등재 2005-01-01 평가 등재학술지 선정 (등재후보2차) KCI등재 2004-01-01 평가 등재후보 1차 PASS (등재후보1차) KCI후보 2003-01-01 평가 등재후보학술지 선정 (신규평가) KCI후보 - 학술지 인용정보
학술지 인용정보 기준연도 WOS-KCI 통합IF(2년) KCIF(2년) KCIF(3년) 2016 0.23 0.23 0.21 KCIF(4년) KCIF(5년) 중심성지수(3년) 즉시성지수 0.2 0.17 0.396 0
서지정보 내보내기(Export)
닫기소장기관 정보
닫기권호소장정보
닫기오류접수
닫기오류 접수 확인
닫기음성서비스 신청
닫기음성서비스 신청 확인
닫기이용약관
닫기학술연구정보서비스 이용약관 (2017년 1월 1일 ~ 현재 적용)
-
제 1 장 총칙
-
제 1 조 (목적)
- 이 약관은 한국교육학술정보원(이하 "교육정보원"라 함)이 제공하는 학술연구정보서비스의 웹사이트(이하 "서비스" 라함)의 이용에 관한 조건 및 절차와 기타 필요한 사항을 규정하는 것을 목적으로 합니다.
-
제 2 조 (약관의 효력과 변경)
- ① 이 약관은 서비스 메뉴에 게시하여 공시함으로써 효력을 발생합니다.
- ② 교육정보원은 합리적 사유가 발생한 경우에는 이 약관을 변경할 수 있으며, 약관을 변경한 경우에는 지체없이 "공지사항"을 통해 공시합니다.
- ③ 이용자는 변경된 약관사항에 동의하지 않으면, 언제나 서비스 이용을 중단하고 이용계약을 해지할 수 있습니다.
-
제 3 조 (약관외 준칙)
- 이 약관에 명시되지 않은 사항은 관계 법령에 규정 되어있을 경우 그 규정에 따르며, 그렇지 않은 경우에는 일반적인 관례에 따릅니다.
-
제 4 조 (용어의 정의)
이 약관에서 사용하는 용어의 정의는 다음과 같습니다.- ① 이용자 : 교육정보원과 이용계약을 체결한 자
- ② 이용자번호(ID) : 이용자 식별과 이용자의 서비스 이용을 위하여 이용계약 체결시 이용자의 선택에 의하여 교육정보원이 부여하는 문자와 숫자의 조합
- ③ 비밀번호 : 이용자 자신의 비밀을 보호하기 위하여 이용자 자신이 설정한 문자와 숫자의 조합
- ④ 단말기 : 서비스 제공을 받기 위해 이용자가 설치한 개인용 컴퓨터 및 모뎀 등의 기기
- ⑤ 서비스 이용 : 이용자가 단말기를 이용하여 교육정보원의 주전산기에 접속하여 교육정보원이 제공하는 정보를 이용하는 것
- ⑥ 이용계약 : 서비스를 제공받기 위하여 이 약관으로 교육정보원과 이용자간의 체결하는 계약을 말함
- ⑦ 마일리지 : RISS 서비스 중 마일리지 적립 가능한 서비스를 이용한 이용자에게 지급되며, RISS가 제공하는 특정 디지털 콘텐츠를 구입하는 데 사용하도록 만들어진 포인트
-
-
제 2 장 서비스 이용 계약
-
제 5 조 (이용계약의 성립)
- ① 이용계약은 이용자의 이용신청에 대한 교육정보원의 이용 승낙에 의하여 성립됩니다.
- ② 제 1항의 규정에 의해 이용자가 이용 신청을 할 때에는 교육정보원이 이용자 관리시 필요로 하는
사항을 전자적방식(교육정보원의 컴퓨터 등 정보처리 장치에 접속하여 데이터를 입력하는 것을 말합니다)
이나 서면으로 하여야 합니다. - ③ 이용계약은 이용자번호 단위로 체결하며, 체결단위는 1 이용자번호 이상이어야 합니다.
- ④ 서비스의 대량이용 등 특별한 서비스 이용에 관한 계약은 별도의 계약으로 합니다.
-
제 6 조 (이용신청)
- ① 서비스를 이용하고자 하는 자는 교육정보원이 지정한 양식에 따라 온라인신청을 이용하여 가입 신청을 해야 합니다.
- ② 이용신청자가 14세 미만인자일 경우에는 친권자(부모, 법정대리인 등)의 동의를 얻어 이용신청을 하여야 합니다.
-
제 7 조 (이용계약 승낙의 유보)
- ① 교육정보원은 다음 각 호에 해당하는 경우에는 이용계약의 승낙을 유보할 수 있습니다.
- 1. 설비에 여유가 없는 경우
- 2. 기술상에 지장이 있는 경우
- 3. 이용계약을 신청한 사람이 14세 미만인 자로 친권자의 동의를 득하지 않았을 경우
- 4. 기타 교육정보원이 서비스의 효율적인 운영 등을 위하여 필요하다고 인정되는 경우
- ② 교육정보원은 다음 각 호에 해당하는 이용계약 신청에 대하여는 이를 거절할 수 있습니다.
- 1. 다른 사람의 명의를 사용하여 이용신청을 하였을 때
- 2. 이용계약 신청서의 내용을 허위로 기재하였을 때
- ① 교육정보원은 다음 각 호에 해당하는 경우에는 이용계약의 승낙을 유보할 수 있습니다.
-
제 8 조 (계약사항의 변경)
이용자는 다음 사항을 변경하고자 하는 경우 서비스에 접속하여 서비스 내의 기능을 이용하여 변경할 수 있습니다.- ① 성명 및 생년월일, 신분, 이메일
- ② 비밀번호
- ③ 자료신청 / 기관회원서비스 권한설정을 위한 이용자정보
- ④ 전화번호 등 개인 연락처
- ⑤ 기타 교육정보원이 인정하는 경미한 사항
-
-
제 3 장 서비스의 이용
-
제 9 조 (서비스 이용시간)
- 서비스의 이용 시간은 교육정보원의 업무 및 기술상 특별한 지장이 없는 한 연중무휴, 1일 24시간(00:00-24:00)을 원칙으로 합니다. 다만 정기점검등의 필요로 교육정보원이 정한 날이나 시간은 그러하지 아니합니다.
-
제 10 조 (이용자번호 등)
- ① 이용자번호 및 비밀번호에 대한 모든 관리책임은 이용자에게 있습니다.
- ② 명백한 사유가 있는 경우를 제외하고는 이용자가 이용자번호를 공유, 양도 또는 변경할 수 없습니다.
- ③ 이용자에게 부여된 이용자번호에 의하여 발생되는 서비스 이용상의 과실 또는 제3자에 의한 부정사용 등에 대한 모든 책임은 이용자에게 있습니다.
-
제 11 조 (서비스 이용의 제한 및 이용계약의 해지)
- ① 이용자가 서비스 이용계약을 해지하고자 하는 때에는 온라인으로 교육정보원에 해지신청을 하여야 합니다.
- ② 교육정보원은 이용자가 다음 각 호에 해당하는 경우 사전통지 없이 이용계약을 해지하거나 전부 또는 일부의 서비스 제공을 중지할 수 있습니다.
- 1. 타인의 이용자번호를 사용한 경우
- 2. 다량의 정보를 전송하여 서비스의 안정적 운영을 방해하는 경우
- 3. 수신자의 의사에 반하는 광고성 정보, 전자우편을 전송하는 경우
- 4. 정보통신설비의 오작동이나 정보 등의 파괴를 유발하는 컴퓨터 바이러스 프로그램등을 유포하는 경우
- 5. 정보통신윤리위원회로부터의 이용제한 요구 대상인 경우
- 6. 선거관리위원회의 유권해석 상의 불법선거운동을 하는 경우
- 7. 서비스를 이용하여 얻은 정보를 교육정보원의 동의 없이 상업적으로 이용하는 경우
- 8. 비실명 이용자번호로 가입되어 있는 경우
- 9. 일정기간 이상 서비스에 로그인하지 않거나 개인정보 수집․이용에 대한 재동의를 하지 않은 경우
- ③ 전항의 규정에 의하여 이용자의 이용을 제한하는 경우와 제한의 종류 및 기간 등 구체적인 기준은 교육정보원의 공지, 서비스 이용안내, 개인정보처리방침 등에서 별도로 정하는 바에 의합니다.
- ④ 해지 처리된 이용자의 정보는 법령의 규정에 의하여 보존할 필요성이 있는 경우를 제외하고 지체 없이 파기합니다.
- ⑤ 해지 처리된 이용자번호의 경우, 재사용이 불가능합니다.
-
제 12 조 (이용자 게시물의 삭제 및 서비스 이용 제한)
- ① 교육정보원은 서비스용 설비의 용량에 여유가 없다고 판단되는 경우 필요에 따라 이용자가 게재 또는 등록한 내용물을 삭제할 수 있습니다.
- ② 교육정보원은 서비스용 설비의 용량에 여유가 없다고 판단되는 경우 이용자의 서비스 이용을 부분적으로 제한할 수 있습니다.
- ③ 제 1 항 및 제 2 항의 경우에는 당해 사항을 사전에 온라인을 통해서 공지합니다.
- ④ 교육정보원은 이용자가 게재 또는 등록하는 서비스내의 내용물이 다음 각호에 해당한다고 판단되는 경우에 이용자에게 사전 통지 없이 삭제할 수 있습니다.
- 1. 다른 이용자 또는 제 3자를 비방하거나 중상모략으로 명예를 손상시키는 경우
- 2. 공공질서 및 미풍양속에 위반되는 내용의 정보, 문장, 도형 등을 유포하는 경우
- 3. 반국가적, 반사회적, 범죄적 행위와 결부된다고 판단되는 경우
- 4. 다른 이용자 또는 제3자의 저작권 등 기타 권리를 침해하는 경우
- 5. 게시 기간이 규정된 기간을 초과한 경우
- 6. 이용자의 조작 미숙이나 광고목적으로 동일한 내용의 게시물을 10회 이상 반복하여 등록하였을 경우
- 7. 기타 관계 법령에 위배된다고 판단되는 경우
-
제 13 조 (서비스 제공의 중지 및 제한)
- ① 교육정보원은 다음 각 호에 해당하는 경우 서비스 제공을 중지할 수 있습니다.
- 1. 서비스용 설비의 보수 또는 공사로 인한 부득이한 경우
- 2. 전기통신사업법에 규정된 기간통신사업자가 전기통신 서비스를 중지했을 때
- ② 교육정보원은 국가비상사태, 서비스 설비의 장애 또는 서비스 이용의 폭주 등으로 서비스 이용에 지장이 있는 때에는 서비스 제공을 중지하거나 제한할 수 있습니다.
- ① 교육정보원은 다음 각 호에 해당하는 경우 서비스 제공을 중지할 수 있습니다.
-
제 14 조 (교육정보원의 의무)
- ① 교육정보원은 교육정보원에 설치된 서비스용 설비를 지속적이고 안정적인 서비스 제공에 적합하도록 유지하여야 하며 서비스용 설비에 장애가 발생하거나 또는 그 설비가 못쓰게 된 경우 그 설비를 수리하거나 복구합니다.
- ② 교육정보원은 서비스 내용의 변경 또는 추가사항이 있는 경우 그 사항을 온라인을 통해 서비스 화면에 공지합니다.
-
제 15 조 (개인정보보호)
- ① 교육정보원은 공공기관의 개인정보보호에 관한 법률, 정보통신이용촉진등에 관한 법률 등 관계법령에 따라 이용신청시 제공받는 이용자의 개인정보 및 서비스 이용중 생성되는 개인정보를 보호하여야 합니다.
- ② 교육정보원의 개인정보보호에 관한 관리책임자는 학술연구정보서비스 이용자 관리담당 부서장(학술정보본부)이며, 주소 및 연락처는 대구광역시 동구 동내로 64(동내동 1119) KERIS빌딩, 전화번호 054-714-0114번, 전자메일 privacy@keris.or.kr 입니다. 개인정보 관리책임자의 성명은 별도로 공지하거나 서비스 안내에 게시합니다.
- ③ 교육정보원은 개인정보를 이용고객의 별도의 동의 없이 제3자에게 제공하지 않습니다. 다만, 다음 각 호의 경우는 이용고객의 별도 동의 없이 제3자에게 이용 고객의 개인정보를 제공할 수 있습니다.
- 1. 수사상의 목적에 따른 수사기관의 서면 요구가 있는 경우에 수사협조의 목적으로 국가 수사 기관에 성명, 주소 등 신상정보를 제공하는 경우
- 2. 신용정보의 이용 및 보호에 관한 법률, 전기통신관련법률 등 법률에 특별한 규정이 있는 경우
- 3. 통계작성, 학술연구 또는 시장조사를 위하여 필요한 경우로서 특정 개인을 식별할 수 없는 형태로 제공하는 경우
- ④ 이용자는 언제나 자신의 개인정보를 열람할 수 있으며, 스스로 오류를 수정할 수 있습니다. 열람 및 수정은 원칙적으로 이용신청과 동일한 방법으로 하며, 자세한 방법은 공지, 이용안내에 정한 바에 따릅니다.
- ⑤ 이용자는 언제나 이용계약을 해지함으로써 개인정보의 수집 및 이용에 대한 동의, 목적 외 사용에 대한 별도 동의, 제3자 제공에 대한 별도 동의를 철회할 수 있습니다. 해지의 방법은 이 약관에서 별도로 규정한 바에 따릅니다.
-
제 16 조 (이용자의 의무)
- ① 이용자는 서비스를 이용할 때 다음 각 호의 행위를 하지 않아야 합니다.
- 1. 다른 이용자의 이용자번호를 부정하게 사용하는 행위
- 2. 서비스를 이용하여 얻은 정보를 교육정보원의 사전승낙없이 이용자의 이용이외의 목적으로 복제하거나 이를 출판, 방송 등에 사용하거나 제3자에게 제공하는 행위
- 3. 다른 이용자 또는 제3자를 비방하거나 중상모략으로 명예를 손상하는 행위
- 4. 공공질서 및 미풍양속에 위배되는 내용의 정보, 문장, 도형 등을 타인에게 유포하는 행위
- 5. 반국가적, 반사회적, 범죄적 행위와 결부된다고 판단되는 행위
- 6. 다른 이용자 또는 제3자의 저작권등 기타 권리를 침해하는 행위
- 7. 기타 관계 법령에 위배되는 행위
- ② 이용자는 이 약관에서 규정하는 사항과 서비스 이용안내 또는 주의사항을 준수하여야 합니다.
- ③ 이용자가 설치하는 단말기 등은 전기통신설비의 기술기준에 관한 규칙이 정하는 기준에 적합하여야 하며, 서비스에 장애를 주지 않아야 합니다.
- ① 이용자는 서비스를 이용할 때 다음 각 호의 행위를 하지 않아야 합니다.
-
제 17 조 (광고의 게재)
교육정보원은 서비스의 운용과 관련하여 서비스화면, 홈페이지, 전자우편 등에 광고 등을 게재할 수 있습니다.
-
-
제 4 장 서비스 이용 요금
-
제 18 조 (이용요금)
- ① 서비스 이용료는 기본적으로 무료로 합니다. 단, 민간업체와의 협약에 의해 RISS를 통해 서비스 되는 콘텐츠의 경우 각 민간 업체의 요금 정책에 따라 유료로 서비스 합니다.
- ② 그 외 교육정보원의 정책에 따라 이용 요금 정책이 변경될 경우에는 온라인으로 서비스 화면에 게시합니다.
-
-
제 5 장 마일리지 정책
-
제 19 조 (마일리지 정책의 변경)
- ① RISS 마일리지는 2017년 1월부로 모두 소멸되었습니다.
- ② 교육정보원은 마일리지 적립ㆍ사용ㆍ소멸 등 정책의 변경에 대해 온라인상에 공지해야하며, 최근에 온라인에 등재된 내용이 이전의 모든 규정과 조건보다 우선합니다.
-
-
제 6 장 저작권
-
제 20 조 (게재된 자료에 대한 권리)
서비스에 게재된 자료에 대한 권리는 다음 각 호와 같습니다.- ① 게시물에 대한 권리와 책임은 게시자에게 있으며, 교육정보원은 게시자의 동의 없이는 이를 영리적 목적으로 사용할 수 없습니다.
- ② 게시자의 사전 동의가 없이는 이용자는 서비스를 이용하여 얻은 정보를 가공, 판매하는 행위 등 서비스에 게재된 자료를 상업적 목적으로 이용할 수 없습니다.
-
-
제 7 장 이의 신청 및 손해배상 청구 금지
-
제 21 조 (이의신청금지)
이용자는 교육정보원에서 제공하는 서비스 이용시 발생되는 어떠한 문제에 대해서도 무료 이용 기간 동안은 이의 신청 및 민원을 제기할 수 없습니다. -
제 22 조 (손해배상청구금지)
이용자는 교육정보원에서 제공하는 서비스 이용시 발생되는 어떠한 문제에 대해서도 무료 이용 기간 동안은 교육정보원 및 관계 기관에 손해배상 청구를 할 수 없으며 교육정보원은 이에 대해 책임을 지지 아니합니다.
-
-
부칙
이 약관은 2000년 6월 1일부터 시행합니다. -
부칙(개정 2005. 5. 31)
이 약관은 2005년 5월 31일부터 시행합니다. -
부칙(개정 2010. 1. 1)
이 약관은 2010년 1월 1일부터 시행합니다. -
부칙(개정 2010. 4 1)
이 약관은 2010년 4월 1일부터 시행합니다. -
부칙(개정 2017. 1 1)
이 약관은 2017년 1월 1일부터 시행합니다.
학술연구정보서비스(이하 RISS)는 정보주체의 자유와 권리 보호를 위해 「개인정보 보호법」 및 관계 법령이 정한 바를 준수하여, 적법하게 개인정보를 처리하고 안전하게 관리하고 있습니다. 이에 「개인정보 보호법」 제30조에 따라 정보주체에게 개인정보 처리에 관한 절차 및 기준을 안내하고, 이와 관련한 고충을 신속하고 원활하게 처리할 수 있도록 하기 위하여 다음과 같이 개인정보 처리방침을 수립·공개합니다.
주요 개인정보 처리 표시(라벨링)
목 차
-
 제1조(개인정보의 처리 목적)
제1조(개인정보의 처리 목적)
-
 제2조(개인정보의 처리 및 보유 기간)
제2조(개인정보의 처리 및 보유 기간)
-
 제3조(처리하는 개인정보의 항목)
제3조(처리하는 개인정보의 항목)
-
 제4조(개인정보파일 등록 현황)
제4조(개인정보파일 등록 현황)
-
 제5조(개인정보의 제3자 제공)
제5조(개인정보의 제3자 제공)
-
 제6조(개인정보 처리업무의 위탁)
제6조(개인정보 처리업무의 위탁)
-
 제7조(개인정보의 파기 절차 및 방법)
제7조(개인정보의 파기 절차 및 방법)
-
 제8조(정보주체와 법정대리인의 권리·의무 및 그 행사 방법)
제8조(정보주체와 법정대리인의 권리·의무 및 그 행사 방법)
-
 제9조(개인정보의 안전성 확보조치)
제9조(개인정보의 안전성 확보조치)
-
 제10조(개인정보 자동 수집 장치의 설치·운영 및 거부)
제10조(개인정보 자동 수집 장치의 설치·운영 및 거부)
-
 제11조(개인정보 보호책임자)
제11조(개인정보 보호책임자)
-
 제12조(개인정보의 열람청구를 접수·처리하는 부서)
제12조(개인정보의 열람청구를 접수·처리하는 부서)
-
 제13조(정보주체의 권익침해에 대한 구제방법)
제13조(정보주체의 권익침해에 대한 구제방법)
-
 제14조(추가적 이용·제공 판단기준)
제14조(추가적 이용·제공 판단기준)
-
 제15조(개인정보 처리방침의 변경)
제15조(개인정보 처리방침의 변경)
-
 제1조(개인정보의 처리 목적)
제1조(개인정보의 처리 목적)
- RISS는 개인정보를 다음의 목적을 위해 처리합니다. 처리하고 있는 개인정보는 다음의 목적 이외의 용도로는 이용되지 않으며, 이용 목적이 변경되는 경우에는 「개인정보 보호법」 제18조에 따라 별도의 동의를 받는 등 필요한 조치를 이행할 예정입니다.
-
가. 서비스 제공
- 콘텐츠 제공, 문헌배송 및 결제, 요금정산 등 서비스 제공
나. 회원관리
- 회원제 서비스 이용에 따른 본인확인,
- 만14세 미만 아동 개인 정보 수집 시 법정 대리인 동의여부 확인, 추후 법정 대리인 본인확인
- 분쟁 조정을 위한 기록보존, 불만처리 등을 위한 원활한 의사소통 경로의 확보, 공지사항 전달
다. 서비스 개선
- 신규 서비스 개발 및 특화
- 통계학적 특성에 따른 서비스 제공 및 광고 게재, 이벤트 등 정보 전달 및 참여 기회 제공
- 서비스 이용에 대한 통계 -
 제2조(개인정보의 처리 및 보유 기간)
제2조(개인정보의 처리 및 보유 기간)
-
가. 처리기간 및 보유 기간:
3년
또는 회원탈퇴시까지
나. 다만, 다음의 사유에 해당하는 경우에는 해당 사유 종료시 까지 정보를 보유 및 열람합니다.
▶ 신청 중인 서비스가 완료 되지 않은 경우
- 보존 이유 : 진행 중인 서비스 완료(예:원문복사 등)
- 보존 기간 : 서비스 완료 시까지
- 열람 예정 시기 : 수시(RISS에서 신청된 서비스의 처리내역 및 진행상태 확인 요청 시)
▶ 관련법령에 의한 정보보유 사유 및 기간
- 대금결제 및 재화 등의 공급에 관한 기록 :5년
(「전자상거래 등에서의 소비자보호에 관한
법률」 제 6조 및 시행령 제 6조)
- 소비자의 불만 또는 분쟁 처리에 관한 기록 :3년
(「전자상거래 등에서의 소비자보호에 관한
법률」 제 6조 및 시행령 제 6조)
- 접속에 관한 기록 :2년
이상(개인정보보호위원회 : 개인정보의 안전성 확보조치 기준) -
 제3조(처리하는 개인정보의 항목)
제3조(처리하는 개인정보의 항목)
-
가. 필수 항목 : ID, 이름, 생년월일, 신분(직업구분), 이메일, 소속분야,
보호자 성명(어린이회원), 보호자 이메일(어린이회원)
나: 선택 항목 : 소속기관명, 학과/부서명, 학번/직원번호, 전화, 주소, 장애인 여부
다. 자동수집항목 : IP주소, ID, 서비스 이용기록, 방문기록 -
 제4조(개인정보파일 등록 현황)
제4조(개인정보파일 등록 현황)
-
개인정보파일의 명칭 운영근거 / 처리목적 개인정보파일에 기록되는 개인정보의 항목 보유기간 학술연구정보서비스 이용자 가입정보 파일 한국교육학술정보원법 필수 ID, 비밀번호, 성명, 생년월일, 신분(직업구분), 이메일, 소속분야, 웹진메일 수신동의 여부 3년
또는
탈퇴시선택 소속기관명, 소속도서관명, 학과/부서명, 학번/직원번호, 휴대전화, 주소 -
 제5조(개인정보의 제3자 제공)
제5조(개인정보의 제3자 제공)
-
가. RISS는 원칙적으로 정보주체의 개인정보를 제1조(개인정보의 처리 목적)에서 명시한 범위 내에서
처리하며, 정보주체의 사전 동의 없이는 본래의 범위를 초과하여 처리하거나 제3자에게 제공하지
않습니다. 단, 정보주체의 동의, 법률의 특별한 규정 등 개인정보 보호법 제17조 및 제18조에 해당하는
경우에만 개인정보를 제3자에게 제공합니다.
나. RISS는 원활한 서비스 제공을 위해 다음의 경우 정보주체의 동의를 얻어 필요 최소한의 범위로만
제공합니다.
- 복사/대출 배송 서비스를 위해서 아래와 같이 개인정보를 제공합니다.
1. 개인정보 제공 대상 : 제공도서관, ㈜이니시스(선불결제 시)
2. 개인정보 제공 목적 : 복사/대출 서비스 제공
3. 개인정보 제공 항목 : 이름, 전화번호, 이메일
4. 개인정보 보유 및 이용 기간 : 신청건 발생일 후 5년
▶ 개인정보 제공에 동의하지 않을 권리가 있으며, 거부하는 경우 서비스 이용이 불가합니다. -
 제6조(개인정보 처리업무의 위탁)
제6조(개인정보 처리업무의 위탁)
- RISS는 원활한 개인정보 업무처리를 위하여 다음과 같이 개인정보 처리업무를 위탁하고 있습니다.
-
가. 위탁하는 업무 내용 : 회원 개인정보 처리
나. 수탁업체명 : ㈜퓨쳐누리 - RISS는 위탁계약 체결 시 「개인정보 보호법」 제26조에 따라 위탁업무 수행 목적 외 개인정보 처리금지, 안전성 확보조치, 재위탁 제한, 수탁자에 대한 관리·감독, 손해배상 등 책임에 관한 사항을 계약서 등 문서에 명시하고, 수탁자가 개인정보를 안전하게 처리하는지를 감독하고 있습니다.
- 위탁업무의 내용이나 수탁자가 변경될 경우에는 지체 없이 본 개인정보 처리방침을 통하여 공개하도록 하겠습니다.
-
 제7조(개인정보의 파기 절차 및 방법)
제7조(개인정보의 파기 절차 및 방법)
-
가. 파기절차
- 개인정보의 파기 : 보유기간이 경과한 개인정보는 종료일로부터 지체 없이 파기
- 개인정보파일의 파기 : 개인정보파일의 처리 목적 달성, 해당 서비스의 폐지, 사업의 종료 등 그
개인정보파일이 불필요하게 되었을 때에는 개인정보의 처리가 불필요한 것으로 인정되는 날로부터
지체 없이 그 개인정보파일을 파기.
나. 파기방법
- 전자적 형태의 정보는 기록을 재생할 수 없는 기술적 방법을 사용하여 파기.
- 종이에 출력된 개인정보는 분쇄기로 분쇄하거나 소각을 통하여 파기. -
 제8조(정보주체와 법정대리인의 권리·의무 및 그 행사 방법)
제8조(정보주체와 법정대리인의 권리·의무 및 그 행사 방법)
-
정보주체(만 14세 미만인 경우에는 법정대리인을 말함)는 개인정보주체로서 다음과 같은 권리를 행사할 수 있습니다.
가. 권리 행사 항목 및 방법
- 권리 행사 항목: 개인정보 열람 요구, 오류 정정 요구, 삭제 요구, 처리정지 요구
- 권리 행사 방법: 개인정보 처리 방법에 관한 고시 별지 제8호(대리인의 경우 제11호) 서식에 따라
작성 후 서면, 전자우편, 모사전송(FAX), 전화, 인터넷(홈페이지 고객센터) 제출
나. 개인정보 열람 및 처리정지 요구는 「개인정보 보호법」 제35조 제5항, 제37조 제2항에 의하여
정보주체의 권리가 제한 될 수 있음
다. 개인정보의 정정 및 삭제 요구는 다른 법령에서 그 개인정보가 수집 대상으로 명시되어 있는 경우에는
그 삭제를 요구할 수 없음
라. RISS는 정보주체 권리에 따른 열람의 요구, 정정·삭제의 요구, 처리정지의 요구 시
열람 등 요구를 한 자가 본인이거나 정당한 대리인인지를 확인함.
마. 정보주체의 권리행사 요구 거절 시 불복을 위한 이의제기 절차는 다음과 같습니다.
1) 해당 부서에서 열람 등 요구에 대한 연기 또는 거절 시 요구 받은 날로부터 10일 이내에 정당한 사유
및 이의제기 방법 등을 통지
2) 해당 부서에서 정보주체의 이의제기 신청 및 접수(서면, 유선, 이메일 등)하여 개인정보보호 담당자가
내용 확인
3) 개인정보관리책임자가 처리결과에 대한 최종 검토
4) 해당부서에서 정보주체에게 처리결과 통보
*. [교육부 개인정보 보호지침 별지 제1호] 개인정보 (열람, 정정·삭제, 처리정지) 요구서
*. [교육부 개인정보 보호지침 별지 제2호] 위임장
-
 제9조(개인정보의 안전성 확보조치)
제9조(개인정보의 안전성 확보조치)
-
가. 내부관리계획의 수립 및 시행 : RISS의 내부관리계획 수립 및 시행은 한국교육학술정보원의 내부
관리 지침을 준수하여 시행.
나. 개인정보 취급 담당자의 최소화 및 교육
- 개인정보를 취급하는 분야별 담당자를 지정․운영
- 한국교육학술정보원의 내부 관리 지침에 따른 교육 실시
다. 개인정보에 대한 접근 제한
- 개인정보를 처리하는 데이터베이스시스템에 대한 접근권한의 부여, 변경, 말소를 통하여
개인정보에 대한 접근통제 실시
- 침입차단시스템, ID/패스워드 및 공인인증서 확인을 통한 접근 통제 등 보안시스템 운영
라. 접속기록의 보관 및 위변조 방지
- 개인정보처리시스템에 접속한 기록(웹 로그, 요약정보 등)을 2년 이상 보관, 관리
- 접속 기록이 위변조 및 도난, 분실되지 않도록 보안기능을 사용
마. 개인정보의 암호화 : 이용자의 개인정보는 암호화 되어 저장 및 관리
바. 해킹 등에 대비한 기술적 대책
- 보안프로그램을 설치하고 주기적인 갱신·점검 실시
- 외부로부터 접근이 통제된 구역에 시스템을 설치하고 기술적/물리적으로 감시 및 차단
사. 비인가자에 대한 출입 통제
- 개인정보를 보관하고 있는 개인정보시스템의 물리적 보관 장소를 별도 설치․운영
- 물리적 보관장소에 대한 출입통제, CCTV 설치․운영 절차를 수립, 운영
-
 제10조(개인정보 자동 수집 장치의 설치·운영 및 거부)
제10조(개인정보 자동 수집 장치의 설치·운영 및 거부)
-
가. 정보주체의 이용정보를 저장하고 수시로 불러오는 ‘쿠키(cookie)’를 사용합니다.
나. 쿠키는 웹사이트를 운영하는데 이용되는 서버(http)가 이용자의 컴퓨터브라우저에게 보내는 소량의
정보이며 이동자들의 PC 컴퓨터내의 하드디스크에 저장되기도 합니다.
1) 쿠키의 사용목적 : 이용자에게 보다 편리한 서비스 제공하기 위해 사용됩니다.
2) 쿠키의 설치·운영 및 거부 : 브라우저 옵션 설정을 통해 쿠키 허용, 쿠키 차단 등의 설정을 할 수
있습니다.
- Internet Explorer : 웹브라우저 우측 상단의 도구 메뉴 > 인터넷 옵션 > 개인정보 > 설정 > 고급
- Edge : 웹브라우저 우측 상단의 설정 메뉴 > 쿠키 및 사이트 권한 > 쿠키 및 사이트 데이터
관리 및 삭제
- Chrome : 웹브라우저 우측 상단의 설정 메뉴 > 보안 및 개인정보 보호 > 쿠키 및 기타 사이트
데이터
3) 쿠키 저장을 거부 또는 차단할 경우 서비스 이용에 어려움이 발생할 수 있습니다. -
 제11조(개인정보 보호책임자)
제11조(개인정보 보호책임자)
-
가. RISS는 개인정보 처리에 관한 업무를 총괄해서 책임지고, 개인정보 처리와 관련한 정보주체의
불만처리 및 피해구제 등을 위하여 아래와 같이 개인정보 보호책임자를 지정하고 있습니다.
구분 담당자 연락처 KERIS 개인정보 보호책임자 정보보호본부 김태우 - 이메일 : lsy@keris.or.kr
- 전화번호 : 053-714-0439
- 팩스번호 : 053-714-0195KERIS 개인정보 보호담당자 개인정보보호부 이상엽 RISS 개인정보 보호책임자 대학학술본부 장금연 - 이메일 : giltizen@keris.or.kr
- 전화번호 : 053-714-0149
- 팩스번호 : 053-714-0194RISS 개인정보 보호담당자 학술진흥부 길원진
나. 정보주체는 RISS의 서비스(또는 사업)을 이용하시면서 발생한 모든 개인정보 보호 관련 문의, 불만처리,
피해구제 등에 관한 사항을 개인정보 보호책임자 및 담당부서로 문의 할 수 있습니다.
RISS는 정보주체의 문의에 대해 답변 및 처리해드릴 것입니다. -
 제12조(개인정보의 열람청구를 접수·처리하는 부서)
제12조(개인정보의 열람청구를 접수·처리하는 부서)
-
가. 자체 개인정보 열람청구 접수ㆍ처리 창구
부서명 : 대학학술본부/학술진흥부
담당자 : 길원진
이메일 : giltizen@keris.or.kr
전화번호 : 053-714-0149
팩스번호 : 053-714-0194
나. 개인정보 열람청구 접수ㆍ처리 창구
- 개인정보보호 포털 웹사이트(www.privacy.go.kr)
- 개인정보보호 포털 → 민원마당 → 개인정보 열람 등 요구(본인확인을 위한
휴대전화·아이핀(I-PIN) 등이 있어야 함) -
 제13조(정보주체의 권익침해에 대한 구제방법)
제13조(정보주체의 권익침해에 대한 구제방법)
-
‣ 정보주체는 개인정보침해로 인한 구제를 받기 위하여 개인정보분쟁조정위원회, 한국인터넷진흥원
개인정보침해신고센터 등에 분쟁해결이나 상담 등을 신청할 수 있습니다. 이 밖에 기타 개인정보
침해의 신고, 상담에 대하여는 아래의 기관에 문의하시기 바랍니다.
가. 개인정보분쟁조정위원회 : (국번없이) 1833-6972(www.kopico.go.kr)
나. 개인정보침해신고센터 : (국번없이) 118(privacy.kisa.or.kr)
다. 대검찰청 : (국번없이) 1301 (www.spo.go.kr)
라. 경찰청 : (국번없이) 182 (ecrm.cyber.go.kr)
‣RISS는 정보주체의 개인정보자기결정권을 보장하고, 개인정보침해로 인한 상담 및 피해 구제를
위해 노력하고 있으며, 신고나 상담이 필요한 경우 아래의 담당부서로 연락해 주시기 바랍니다.
▶ 개인정보 관련 고객 상담 및 신고
부서명 : 학술진흥부
담당자 : 길원진
연락처 : ☎053-714-0149 / (Mail) giltizen@keris.or.kr / (Fax) 053-714-0194
‣「개인정보 보호법」제35조(개인정보의 열람), 제36조(개인정보의 정정·삭제), 제37조(개인정보의
처리정지 등)의 규정에 의한 요구에 대하여 공공기관의 장이 행한 처분 또는 부작위로 인하여 권리
또는 이익의 침해를 받은 자는 행정심판법이 정하는 바에 따라 행정심판을 청구할 수 있습니다.
※ 행정심판에 대해 자세한 사항은 중앙행정심판위원회(www.simpan.go.kr) 홈페이지를 참고
하시기 바랍니다. -
 제14조(추가적인 이용ㆍ제공 판단기준)
제14조(추가적인 이용ㆍ제공 판단기준)
-
RISS는 「개인정보 보호법」제15조제3항 및 제17조제4항에 따라 「개인정보 보호법 시행령」
제14조의2에 따른 사항을 고려하여 정보주체의 동의 없이 개인정보를 추가적으로 이용 · 제공할 수 있습니다.
이에 따라 RISS는 정보주체의 동의 없이 추가적인 이용 · 제공을 하는 경우, 본 개인정보처리방침을
통해 아래와 같은 추가적인 이용 · 제공을 위한 고려사항에 대한 판단기준을 안내드리겠습니다.
▶ 개인정보를 추가적으로 이용 · 제공하려는 목적이 당초 수집 목적과 관련성이 있는지 여부
▶ 개인정보를 수집한 정황 또는 처리 관행에 비추어 볼 때 추가적인 이용 · 제공에 대한 예측
가능성이 있는지 여부
▶ 개인정보의 추가적인 이용 · 제공이 정보주체의 이익을 부당하게 침해하는지 여부
▶ 가명처리 또는 암호화 등 안전성 확보에 필요한 조치를 하였는지 여부 -
 제15조(개인정보 처리방침의 변경)
제15조(개인정보 처리방침의 변경)
-
RISS는 「개인정보 보호법」제30조에 따라 개인정보 처리방침을 변경하는 경우 정보주체가 쉽게
확인할 수 있도록 홈페이지에 공개하고 변경이력을 관리하고 있습니다.
‣ 이 개인정보처리방침은 2023. 1. 31. 부터 적용됩니다.
‣ 이전의 개인정보처리방침은 상단에서 확인할 수 있습니다.
자동로그아웃 안내
닫기인증오류 안내
닫기귀하께서는 휴면계정 전환 후 1년동안 회원정보 수집 및 이용에 대한
재동의를 하지 않으신 관계로 개인정보가 삭제되었습니다.
(참조 : RISS 이용약관 및 개인정보처리방침)
신규회원으로 가입하여 이용 부탁 드리며, 추가 문의는 고객센터로 연락 바랍니다.
- 기존 아이디 재사용 불가
휴면계정 안내
RISS는 [표준개인정보 보호지침]에 따라 2년을 주기로 개인정보 수집·이용에 관하여 (재)동의를 받고 있으며, (재)동의를 하지 않을 경우, 휴면계정으로 전환됩니다.
(※ 휴면계정은 원문이용 및 복사/대출 서비스를 이용할 수 없습니다.)
휴면계정으로 전환된 후 1년간 회원정보 수집·이용에 대한 재동의를 하지 않을 경우, RISS에서 자동탈퇴 및 개인정보가 삭제처리 됩니다.
고객센터 1599-3122
ARS번호+1번(회원가입 및 정보수정)